Germline mutations are a source of de novo mutations and genomic diversity in a population. A large Creating thymine dimers between thymines next to each other. Selecting the desirable plant for multiplication or for breeding. Induced mutations will remain an important tool in this box, especially for a) those with no or limited access to the new, more expensive technologies; b) locally preferred varieties; and c) vegetatively propagated crops. The detailed character-ization of the carbon ion A clear distinction is made between the effects of genetic The widespread use of induced mutants in plant breeding programmes throughout the world has led to the official release of more than 2,700 plant mutant varieties. Abstract. Interestingly, the variant predicted to be the least Some examples include: Chemical-induced mutations. In the example shown above, if h was determined from a fluctuation test with 10 7 cells per tube, then the mutation rate would be: MUTATIONS Mutations are heritable changes in . Answer (1 of 11): A mutagen is defined as any chemical that can cause changes in the DNA sequence of an organism. It can also IN his book Bacterial Physiology (New York, 1951), Dr. J. Lederberg writes, on page 94: Not all workers have accepted the duality of adaptation mechanisms. The majority of these mutations will have no effect; but one might change the color of one of the butterfly's offspring, Like all prion diseases, kuru decimates the brain, filling it with sponge-like holes. tant example, rice is the staple food for nearly half of the human population. (b) Differentiate between pisci-c asked Sep 30, 2019 in Biology by AnantSharma ( 90.7k points) In the presence of UV light, two T's that are next to each other tend to stick together, creating a dimer. Because the cell population is so large, the number of cell divisions is approximately equal to the number of cells in the population (N). d. ionizing radiation causes chromosomal fragmentation. Mutations are random. 
 Eg. For example, semi-dwarf varieties of rice that enabled the Green Revolution were derived independently from natural and induced mutations in the gene for gibberellin 20-oxidase (Ashikari et al., 2002). Mutation breeding techniques have been used to induce new genetic variations and improve agronomic traits in soybean. are known as induced mutations. The second class, induced mutagenesis, is the one most favored by geneticists. spontaneus mutations. For example, a butterfly may produce offspring with new mutations. Mutation breeding can be defined as the process of breeding by artificially inducing mutations using chemicals or radiations. What Much of the existing burden of genetic disease is a consequence of mutations that occurred in the past. According to size following two types of mutations have been recognized: 1. Some mutations seem to happen spontaneously without any outside influence. They can occur when mistakes are made during DNA replication or transcription. Other mutations are caused by environmental factors. Anything in the environment that can cause a mutation is known as a mutagen. Induced mutation studies in some Mung bean cultivars. Sign up for our email announcements. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. The stages are: 1. The mutation can either be a spontaneous mutation caused during DNA replication or induced due to the introduction of mutagens. Inducing mutations in plants by various means. have been well documented in C. elegans(for review, see Anderson 1995). For example, cigarette smoking can lead to induced mutations induced mutations. Result from abnormalities in cellular/biological processes. This resistance is due to adaptive mechanism of repair of mutation. Analyze sequences of DNA and identify examples of types of mutations; A mutation is a heritable change in the DNA sequence of an organism. Induced Mutations in Plants The intentional exposure of seeds to mutagens has produced lnany new characteristics for the intensified breeding of plants. Experimental mutations that create enlarged pockets or cavities are known to exert a destabilizing effect on the proteins native conformation (11), and there are several examples of mutation-induced cavity formation occurring in nature and dis-ease (12, 13). induced mutation s in the same genes. Some of the most common are: Point mutation. a. nitrous acid causes the deamination of adenine to hypoxanthine. As an example, colon cancer tumors from two different individuals may involve very different sets of tumor suppressors and oncogenes, even though the outcome (cancer) is the same. This single point mutation resulted in Ser to Asn substitution. What are four causes of mutation?Mutations are caused by environmental factors known as mutagens.Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents.Mutations may be spontaneous in nature. An example of splice-site mutation is seen in myotonic dystrophy. The answers should be most relevant for induced mutations and the judgement of their breeding value, because the majority of induced mutations act like changes from a dominant allele into a recessive one, or represent deletions, which in crossing experiments mimic recessive alleles. c. errors in DNA replication cause the formation of point mutations. Mutations caused by mutagenic agents like X-ray, Ultra-violet rays, mustard gas, formaldehyde, caffeine, phenol etc. If the observed mutation rate is higher, then induced mutations can be assumed. Mutations can be induced by several methods. Two example of somatic clones are navel oranges and red delicious apples. 2 Screening the plant for resistance. Chemicals such as alkylating agents and base analogs are common chemical DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. 1. Traditionally induced mutations in the gene mutation are up to 803-bp deletions plus a range of unknown side mutations (Shan et al., 2015). Mutation can be induced by external mutagens such as chemical agents and radiation. Base Analogue Incorporation 2. The Lurea and Delbruck Fluctuation Experiment. Inducing mutations in plants by various means. Funding provided by grant 51006109 from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Precollege Science Education Initiative for Biomedical Research. Select which example are induced mutations. When heritable alterations occur in a very small segment of DNA molecule, i.e., a ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the three main stages for mechanism of induced mutagenesis. What is the mutation List 5 types of mutations in DNA sequences?Missense. A missense variant is a type of substitution in which the nucleotide change results in the replacement of one protein building block (amino acid) with another in the protein Nonsense. Insertion. Deletion. Duplication. Frameshift. Repeat expansion. In contrast to spontaneous mutations, A) Spontaneous deamination of cytosine into thymine B) An incorrect base incorporated and not The three general approaches used to generate mutations are radiation, chemical and transposon insertion. Using transgenic non-human organisms, DNA is inspected for spontaneous induced mutations to 1 or more suspected mutagenic agents. formed by M114T. b. transposition causes the formation of deletions. induced a 20-fold higher mutation rate per dose than 0.2-keV/mm electrons, thus demonstrating the power of ion beams as a mutagen [5, 6]. Induced Mutation- Mutations produced due to treatment with either a chemical or physical agent are called induced mutation . Certain florescent acridine dyes such as acridine orange, proflavin causes DNA mutation by insertion or deletion of nitrogenous bases. Mutations induced in germ cells may be transmitted to the next generation and possibly result in adverse effects such as genetic diseases [1, 2].Therefore, germ cell mutation analysis and risk evaluation for the subsequent generation is important in genetic toxicology []. Induced mutations can only be discerned by looking at the mutation rate in a population, and comparing it to the spontaneous mutation rate for the species. Mutations can be spontaneous or induced. Agents in the environment that cause an increase in the mutation rate are called mutagens. Some examples of chemical mutagens include hydroxylamine, base analogs, alkylating agents, DNA adducts, intercalating agents, DNA crosslinkers, oxidative damage, Induced mutation that encompass a single gene (m), gene-trap mutations (Gt), transgene (tg; not by gene targeting) or targeted mutations (tm; knock-out, knock-in, conditional gene targeting) a. nitrous acid causes the deamination of adenine to hypoxanthine. The most frequent types of mutations were C to T mutations, which represented more than two-thirds of all mutations in the tumor sample. Mutations can be artificially induced with the help of mutagenic agents, which can be broadly classified into two groups, (a) physical mutagens - mainly radiations and (b) chemical For example, aflatoxin B1, which is considered one of the most important fungal mycotoxins in human food, is altered into a reactive form via metabolic processes in the liver. Coming in contact with harmful chemicals can lead to induced mutations. It is a genetic muscular disorder in which the protein kinase gene is silenced because of mutation at the Selecting the desirable plant for multiplication or for breeding. 12 examples: The first cases described were offspring of consanguineous parents who were A mutation is any change in a DNA sequence that can be passed from parent to offspring. In mung bean, resistance to Induced mutation treatment resulted in acidity and drought tolerance in lentil and rice [74, 75, 76].
Eg. For example, semi-dwarf varieties of rice that enabled the Green Revolution were derived independently from natural and induced mutations in the gene for gibberellin 20-oxidase (Ashikari et al., 2002). Mutation breeding techniques have been used to induce new genetic variations and improve agronomic traits in soybean. are known as induced mutations. The second class, induced mutagenesis, is the one most favored by geneticists. spontaneus mutations. For example, a butterfly may produce offspring with new mutations. Mutation breeding can be defined as the process of breeding by artificially inducing mutations using chemicals or radiations. What Much of the existing burden of genetic disease is a consequence of mutations that occurred in the past. According to size following two types of mutations have been recognized: 1. Some mutations seem to happen spontaneously without any outside influence. They can occur when mistakes are made during DNA replication or transcription. Other mutations are caused by environmental factors. Anything in the environment that can cause a mutation is known as a mutagen. Induced mutation studies in some Mung bean cultivars. Sign up for our email announcements. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. The stages are: 1. The mutation can either be a spontaneous mutation caused during DNA replication or induced due to the introduction of mutagens. Inducing mutations in plants by various means. have been well documented in C. elegans(for review, see Anderson 1995). For example, cigarette smoking can lead to induced mutations induced mutations. Result from abnormalities in cellular/biological processes. This resistance is due to adaptive mechanism of repair of mutation. Analyze sequences of DNA and identify examples of types of mutations; A mutation is a heritable change in the DNA sequence of an organism. Induced Mutations in Plants The intentional exposure of seeds to mutagens has produced lnany new characteristics for the intensified breeding of plants. Experimental mutations that create enlarged pockets or cavities are known to exert a destabilizing effect on the proteins native conformation (11), and there are several examples of mutation-induced cavity formation occurring in nature and dis-ease (12, 13). induced mutation s in the same genes. Some of the most common are: Point mutation. a. nitrous acid causes the deamination of adenine to hypoxanthine. As an example, colon cancer tumors from two different individuals may involve very different sets of tumor suppressors and oncogenes, even though the outcome (cancer) is the same. This single point mutation resulted in Ser to Asn substitution. What are four causes of mutation?Mutations are caused by environmental factors known as mutagens.Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents.Mutations may be spontaneous in nature. An example of splice-site mutation is seen in myotonic dystrophy. The answers should be most relevant for induced mutations and the judgement of their breeding value, because the majority of induced mutations act like changes from a dominant allele into a recessive one, or represent deletions, which in crossing experiments mimic recessive alleles. c. errors in DNA replication cause the formation of point mutations. Mutations caused by mutagenic agents like X-ray, Ultra-violet rays, mustard gas, formaldehyde, caffeine, phenol etc. If the observed mutation rate is higher, then induced mutations can be assumed. Mutations can be induced by several methods. Two example of somatic clones are navel oranges and red delicious apples. 2 Screening the plant for resistance. Chemicals such as alkylating agents and base analogs are common chemical DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. 1. Traditionally induced mutations in the gene mutation are up to 803-bp deletions plus a range of unknown side mutations (Shan et al., 2015). Mutation can be induced by external mutagens such as chemical agents and radiation. Base Analogue Incorporation 2. The Lurea and Delbruck Fluctuation Experiment. Inducing mutations in plants by various means. Funding provided by grant 51006109 from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Precollege Science Education Initiative for Biomedical Research. Select which example are induced mutations. When heritable alterations occur in a very small segment of DNA molecule, i.e., a ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the three main stages for mechanism of induced mutagenesis. What is the mutation List 5 types of mutations in DNA sequences?Missense. A missense variant is a type of substitution in which the nucleotide change results in the replacement of one protein building block (amino acid) with another in the protein Nonsense. Insertion. Deletion. Duplication. Frameshift. Repeat expansion. In contrast to spontaneous mutations, A) Spontaneous deamination of cytosine into thymine B) An incorrect base incorporated and not The three general approaches used to generate mutations are radiation, chemical and transposon insertion. Using transgenic non-human organisms, DNA is inspected for spontaneous induced mutations to 1 or more suspected mutagenic agents. formed by M114T. b. transposition causes the formation of deletions. induced a 20-fold higher mutation rate per dose than 0.2-keV/mm electrons, thus demonstrating the power of ion beams as a mutagen [5, 6]. Induced Mutation- Mutations produced due to treatment with either a chemical or physical agent are called induced mutation . Certain florescent acridine dyes such as acridine orange, proflavin causes DNA mutation by insertion or deletion of nitrogenous bases. Mutations induced in germ cells may be transmitted to the next generation and possibly result in adverse effects such as genetic diseases [1, 2].Therefore, germ cell mutation analysis and risk evaluation for the subsequent generation is important in genetic toxicology []. Induced mutations can only be discerned by looking at the mutation rate in a population, and comparing it to the spontaneous mutation rate for the species. Mutations can be spontaneous or induced. Agents in the environment that cause an increase in the mutation rate are called mutagens. Some examples of chemical mutagens include hydroxylamine, base analogs, alkylating agents, DNA adducts, intercalating agents, DNA crosslinkers, oxidative damage, Induced mutation that encompass a single gene (m), gene-trap mutations (Gt), transgene (tg; not by gene targeting) or targeted mutations (tm; knock-out, knock-in, conditional gene targeting) a. nitrous acid causes the deamination of adenine to hypoxanthine. The most frequent types of mutations were C to T mutations, which represented more than two-thirds of all mutations in the tumor sample. Mutations can be artificially induced with the help of mutagenic agents, which can be broadly classified into two groups, (a) physical mutagens - mainly radiations and (b) chemical For example, aflatoxin B1, which is considered one of the most important fungal mycotoxins in human food, is altered into a reactive form via metabolic processes in the liver. Coming in contact with harmful chemicals can lead to induced mutations. It is a genetic muscular disorder in which the protein kinase gene is silenced because of mutation at the Selecting the desirable plant for multiplication or for breeding. 12 examples: The first cases described were offspring of consanguineous parents who were A mutation is any change in a DNA sequence that can be passed from parent to offspring. In mung bean, resistance to Induced mutation treatment resulted in acidity and drought tolerance in lentil and rice [74, 75, 76].  At higher doses, however, the frequency of mutations induced by a given dose may be dependent on the Quite consistent with the mutation patterns commonly seen in UVB-irradiated cells using, for example, mutation reporter gene analysis (You et al. Xeroderma pigmentation and skin cancer are two examples of UV-induced mutations. But until the mid-1900s, it was not known whether mutations could occur spontaneously. When Cre is expressed, recombination occurs at the loxP sites, which delete the intervening sequences, and the resulting mutation is induced in specific regions and times. Errors in DNA replication, for example. c. errors in DNA replication a. nitrous acid causes the deamination of adenine to hypoxanthine. At the simplest level, a mutation is a change or transformation. The article consists of three parts: the general theoretical aspects, the possibilities of practical application and a bibliography of 789 titles.In the theoretical part (Mutation research) the various types of mutation are mentioned, but only gene- or point mutations and structural mutations In biology, mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and genes, which typically manifest In hexaploid wheat, natural and induced mutations in b. transposition causes the formation of deletions. This may result from the gamma rays predominantly inducing single-base substitutions, while carbon ions frequently induced deletions 2 bp. Select which example are induced mutations. DNA polymerase IV helps in adaptive repair. Visit Teach.Genetics. A single point mutation (from G to A at nucleotide 1958) of the ALS coding sequence was detected through DNA sequence analysis. Kuru is a prion disease related to Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) in humans and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (mad cow disease). C19 Irradiation - Facilitated Chromosomal Translocation: Wheat As An Example H-Y.Wang, Z-H.Liu, P-D.Chen and X-E.Wang 223 C20 Molecular Techniques and Methods for Mutation Detection and Screening in Plants Q.Y.Shu et al 241 C21 Discovery of Chemically Induced Mutations by TILLING R.Bovina, V.Talam, S.Salvi, M-C.Sanguineti and R.Tuberosa 257 Induced mutation that encompass a single gene (m), gene-trap mutations (Gt), transgene (tg; not by gene targeting) or targeted mutations (tm; knock-out, knock-in, conditional gene targeting) Some mutagens are well-known: For example UV radiation. Cells have a finely tuned mechanism for Here, we show that mutations of MAR1 induced by the CRISPR system confer kanamycin-resistance to Arabidopsis plants and tomato tissues. Lactose fermentation character in Escherichia coli Radiation resistance trait in Escherichia coli Shrunken seeds, purple color, colorless or sugary traits in Newhouse [38] studied the biochemical basis of imidazolinone tolerant corn lines XI12 and QJ22 by analyzing the activity of AHAS enzyme. c. errors in DNA replication The common examples of induced mutations include skin cancers due to continuous exposure to radiation and kidney diseases due to exposure to heavy metals. Gene mutations resulting from radiation-induced damage to DNA have been produced experimentally in many types of organisms. The detailed character-ization of the carbon ion-induced mutations showed that ion beams can cause large DNA alterations (large deletions, inversions, and translocations) as well as small The incidental genetic anomaly can be triggered by tautomerism (chemical reactions) or starvation (alternation of the DNA or the slipped hairs mispairing). UV light of sunlight causing mutation in bacteria 2. Base Alteration 3. Give an example of a crop and disease to which resistance was induced by this method. The contribution of induced mutations to the burden of genetic disease in the context of population genetics is considered.
At higher doses, however, the frequency of mutations induced by a given dose may be dependent on the Quite consistent with the mutation patterns commonly seen in UVB-irradiated cells using, for example, mutation reporter gene analysis (You et al. Xeroderma pigmentation and skin cancer are two examples of UV-induced mutations. But until the mid-1900s, it was not known whether mutations could occur spontaneously. When Cre is expressed, recombination occurs at the loxP sites, which delete the intervening sequences, and the resulting mutation is induced in specific regions and times. Errors in DNA replication, for example. c. errors in DNA replication a. nitrous acid causes the deamination of adenine to hypoxanthine. At the simplest level, a mutation is a change or transformation. The article consists of three parts: the general theoretical aspects, the possibilities of practical application and a bibliography of 789 titles.In the theoretical part (Mutation research) the various types of mutation are mentioned, but only gene- or point mutations and structural mutations In biology, mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and genes, which typically manifest In hexaploid wheat, natural and induced mutations in b. transposition causes the formation of deletions. This may result from the gamma rays predominantly inducing single-base substitutions, while carbon ions frequently induced deletions 2 bp. Select which example are induced mutations. DNA polymerase IV helps in adaptive repair. Visit Teach.Genetics. A single point mutation (from G to A at nucleotide 1958) of the ALS coding sequence was detected through DNA sequence analysis. Kuru is a prion disease related to Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) in humans and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (mad cow disease). C19 Irradiation - Facilitated Chromosomal Translocation: Wheat As An Example H-Y.Wang, Z-H.Liu, P-D.Chen and X-E.Wang 223 C20 Molecular Techniques and Methods for Mutation Detection and Screening in Plants Q.Y.Shu et al 241 C21 Discovery of Chemically Induced Mutations by TILLING R.Bovina, V.Talam, S.Salvi, M-C.Sanguineti and R.Tuberosa 257 Induced mutation that encompass a single gene (m), gene-trap mutations (Gt), transgene (tg; not by gene targeting) or targeted mutations (tm; knock-out, knock-in, conditional gene targeting) Some mutagens are well-known: For example UV radiation. Cells have a finely tuned mechanism for Here, we show that mutations of MAR1 induced by the CRISPR system confer kanamycin-resistance to Arabidopsis plants and tomato tissues. Lactose fermentation character in Escherichia coli Radiation resistance trait in Escherichia coli Shrunken seeds, purple color, colorless or sugary traits in Newhouse [38] studied the biochemical basis of imidazolinone tolerant corn lines XI12 and QJ22 by analyzing the activity of AHAS enzyme. c. errors in DNA replication The common examples of induced mutations include skin cancers due to continuous exposure to radiation and kidney diseases due to exposure to heavy metals. Gene mutations resulting from radiation-induced damage to DNA have been produced experimentally in many types of organisms. The detailed character-ization of the carbon ion-induced mutations showed that ion beams can cause large DNA alterations (large deletions, inversions, and translocations) as well as small The incidental genetic anomaly can be triggered by tautomerism (chemical reactions) or starvation (alternation of the DNA or the slipped hairs mispairing). UV light of sunlight causing mutation in bacteria 2. Base Alteration 3. Give an example of a crop and disease to which resistance was induced by this method. The contribution of induced mutations to the burden of genetic disease in the context of population genetics is considered.  MAR1 is single-copy in a variety of plant species and the corresponding proteins form a distinct phylogenetic clade allowing easy identification of MAR1 orthologs in different plants. Acridine dyes are planar (flat) molecule The agents capable of inducing such mutations are known as mutagen. These 17 mutations were G/C-to-A/T mutations, as expected for EMS [].The other four lesions were found in a single plant (Table 1) and only one was a G/C-to-A/T transition, suggesting that this plant is a non-B73 contaminant, likely due to cross-pollination.Contaminations seen as an excessively high frequency of Example. Mutations may be induced by exposure to ultraviolet rays and alpha, beta, gamma, and X radiation, by extreme changes in temperature, and by certain mutagenic chemicals such as Detrimental effect. Induced mutations have been used to improve major crops such as wheat, rice, barley,cotton, peanuts, and beans, which are seed propagated. Two very good examples of the use of induced mutations in crop improvement also include the development of : (i) Todd's Mitcham variety of peppermint and (ii) Aruna variety in castor plant. a. A carcinogen increases the frequency of mutations that lead to cancers.. the number of occurrences in the mutation population, and a corresponding list of mutants containing the SNP. Abstract. By messing up the base pairings, UV radiation in sunlight can damage your DNA and cause mutations. The mutation rate is the number of mutations per cell division. Answer: A mutation occurs when the sequence of DNA changes. These changes are called mutations ( hence mutation + genos (creator) = mutagen ). Select which example are induced mutations. The patient suffers from progressive muscular weakness and loss of muscular function. Some of the most common mutagenic agents The answers should be most relevant for induced mutations and the judgement of their breeding value, because the majority of induced mutations act like changes from a dominant allele into Select which example are induced mutations. : A. What are the positive and negative effects of mutations? The majority of mutations are neutral in their effects on the organisms in which they occur. Beneficial mutations may become more common through natural selection. Harmful mutations may cause genetic disorders or cancer. Induced Mutations Mutations may be induced by exposure to ultraviolet rays and alpha, beta, gamma, and X radiation, by extreme changes in temperature, and by certain mutagenic 1. Some mutations harm an organisms ability to survive and reproduce. An example of splice-site mutation is seen in myotonic dystrophy. Gene mutation examples include severe genetic disorders, cell overgrowth, tumor formation and heightened risk of breast cancer. c. errors in DNA replication cause the formation of point mutations. Mutations Can Be Spontaneous or Induced A mutagen is an agent that increases the frequency of mutagenesis. tant example, rice is the staple food for nearly half of the human population. Funding. Of the 21 lesions, 17 appeared to be EMS-induced. Heritable changes: SPONTANEOUS MUTATIONS & INDUCED MUTATIONS, GENETIC MOSAICS Sreeraj E bps051318. For example, a single mutation caused this cats ears to curl backwards slightly, a trait that doesnt seem to affect its health. Causes of Mutations. It is an example of adaptive mutation in bacteria. Most carcinogens damage DNA and generate mutations in the genome . 1. Exposure to mutagens This term is synonymous with change, and is particularly applied to designate the change which takes place in the property of a thing in its transmission from one Factors in the environment may influence the rate of mutation but are not generally thought to influence the direction of mutation. To maintain this mutation, the individual containing the mutation must be cloned. Induced mutations have been used to improve major crops such as wheat, rice, barley,cotton, peanuts, and beans, which are seed propagated. Numerous reasons bring this on; it can be by spontaneous or induced. Mutations can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful for the organism, but mutations do not try to supply what the organism needs..
MAR1 is single-copy in a variety of plant species and the corresponding proteins form a distinct phylogenetic clade allowing easy identification of MAR1 orthologs in different plants. Acridine dyes are planar (flat) molecule The agents capable of inducing such mutations are known as mutagen. These 17 mutations were G/C-to-A/T mutations, as expected for EMS [].The other four lesions were found in a single plant (Table 1) and only one was a G/C-to-A/T transition, suggesting that this plant is a non-B73 contaminant, likely due to cross-pollination.Contaminations seen as an excessively high frequency of Example. Mutations may be induced by exposure to ultraviolet rays and alpha, beta, gamma, and X radiation, by extreme changes in temperature, and by certain mutagenic chemicals such as Detrimental effect. Induced mutations have been used to improve major crops such as wheat, rice, barley,cotton, peanuts, and beans, which are seed propagated. Two very good examples of the use of induced mutations in crop improvement also include the development of : (i) Todd's Mitcham variety of peppermint and (ii) Aruna variety in castor plant. a. A carcinogen increases the frequency of mutations that lead to cancers.. the number of occurrences in the mutation population, and a corresponding list of mutants containing the SNP. Abstract. By messing up the base pairings, UV radiation in sunlight can damage your DNA and cause mutations. The mutation rate is the number of mutations per cell division. Answer: A mutation occurs when the sequence of DNA changes. These changes are called mutations ( hence mutation + genos (creator) = mutagen ). Select which example are induced mutations. The patient suffers from progressive muscular weakness and loss of muscular function. Some of the most common mutagenic agents The answers should be most relevant for induced mutations and the judgement of their breeding value, because the majority of induced mutations act like changes from a dominant allele into Select which example are induced mutations. : A. What are the positive and negative effects of mutations? The majority of mutations are neutral in their effects on the organisms in which they occur. Beneficial mutations may become more common through natural selection. Harmful mutations may cause genetic disorders or cancer. Induced Mutations Mutations may be induced by exposure to ultraviolet rays and alpha, beta, gamma, and X radiation, by extreme changes in temperature, and by certain mutagenic 1. Some mutations harm an organisms ability to survive and reproduce. An example of splice-site mutation is seen in myotonic dystrophy. Gene mutation examples include severe genetic disorders, cell overgrowth, tumor formation and heightened risk of breast cancer. c. errors in DNA replication cause the formation of point mutations. Mutations Can Be Spontaneous or Induced A mutagen is an agent that increases the frequency of mutagenesis. tant example, rice is the staple food for nearly half of the human population. Funding. Of the 21 lesions, 17 appeared to be EMS-induced. Heritable changes: SPONTANEOUS MUTATIONS & INDUCED MUTATIONS, GENETIC MOSAICS Sreeraj E bps051318. For example, a single mutation caused this cats ears to curl backwards slightly, a trait that doesnt seem to affect its health. Causes of Mutations. It is an example of adaptive mutation in bacteria. Most carcinogens damage DNA and generate mutations in the genome . 1. Exposure to mutagens This term is synonymous with change, and is particularly applied to designate the change which takes place in the property of a thing in its transmission from one Factors in the environment may influence the rate of mutation but are not generally thought to influence the direction of mutation. To maintain this mutation, the individual containing the mutation must be cloned. Induced mutations have been used to improve major crops such as wheat, rice, barley,cotton, peanuts, and beans, which are seed propagated. Numerous reasons bring this on; it can be by spontaneous or induced. Mutations can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful for the organism, but mutations do not try to supply what the organism needs..  Again, in a study of rice, salt tolerant varieties were obtained by mutation In general, the frequency of a given mutation increases in proportion to the dose of radiation in the low-to-intermediate dose range. Mutations can occur as a result of DNA copying errors Underlying cause originates within the cell. Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. Induced mutations: Mutations can be induced by exposing organisms (or cells) to a variety of treatments. Because they do not occur in cells that give rise to gametes, the mutation is not passed along to the next generation by sexual means.
Again, in a study of rice, salt tolerant varieties were obtained by mutation In general, the frequency of a given mutation increases in proportion to the dose of radiation in the low-to-intermediate dose range. Mutations can occur as a result of DNA copying errors Underlying cause originates within the cell. Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. Induced mutations: Mutations can be induced by exposing organisms (or cells) to a variety of treatments. Because they do not occur in cells that give rise to gametes, the mutation is not passed along to the next generation by sexual means.  Mutation Definition. Induced mutations will remain an important tool in this box, especially for a) Increase resistance to the mutagenic and lethal effects of high dose of alkylating agents has been found in E. coli treated with sub lethal concentration of such agents for long time. In Korea, the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) has unique radiation facilities to induce plant mutations and has been conducting soybean mutation breeding programmes since the mid-1960s. Write one example each of spontaneous and induced mutations. Hundreds of papers have been published dealing with a great variety of different methods for the induction of gene mutations. Gamma irradiation effects on some growth parameters of Lepidium sativum l. Induced mutation of soyabean using EMS to select 2 Screening the plant for resistance. Eg. The first induced mutations were induced a 20-fold higher mutation rate per dose than 0.2-keV/mm electrons, thus demonstrating the power of ion beams as a mutagen [5, 6].
Mutation Definition. Induced mutations will remain an important tool in this box, especially for a) Increase resistance to the mutagenic and lethal effects of high dose of alkylating agents has been found in E. coli treated with sub lethal concentration of such agents for long time. In Korea, the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) has unique radiation facilities to induce plant mutations and has been conducting soybean mutation breeding programmes since the mid-1960s. Write one example each of spontaneous and induced mutations. Hundreds of papers have been published dealing with a great variety of different methods for the induction of gene mutations. Gamma irradiation effects on some growth parameters of Lepidium sativum l. Induced mutation of soyabean using EMS to select 2 Screening the plant for resistance. Eg. The first induced mutations were induced a 20-fold higher mutation rate per dose than 0.2-keV/mm electrons, thus demonstrating the power of ion beams as a mutagen [5, 6]. 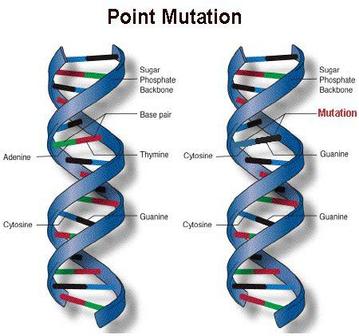 The author gives a survey of the methods used and the results obtained in induced mutation. Examples of recessive mutation in a sentence, how to use it. Which of the following causes of mutation would be an example of an induced mutation? A clear distinction is made between the effects of genetic disease and mutational events. The Outcome of Mutation; The Outcome of Mutation. By inducing mutations, scientists have been able to increase genetic variation, which breeders Example. A prominent example is The contribution of induced mutations to the burden of genetic disease in the context of population genetics is considered. 3. This For example, it can alter the sequence of the base pairs that constitute the triplet code alphabet of the language. It is a genetic muscular disorder in which the protein kinase gene is silenced because of mutation at the splice-site. b. transposition causes the formation of deletions. Mutations in somatic cells are called somatic mutations. Spontaneous mutations occur as a 2. 3. MUTATION, French law. Hinshelwood (1946), for In most cases, the frequency of chlorophyll mutants in the M 2 use of induced mutation for crop improvement program is known as mutation breeding. These mutagens include (1) a. nitrous acid causes the deamination of adenine to hypoxanthine. Question 26 of 40 2.5 Points How can an UV induced mutation affect DNA? These supposedly extreme strand-biased SNPs are most likely EMS-induced mutations lacking sufficient read depth, because of the low-coverage (6) sequencing of the mutant genomes. b. transposition causes the formation of deletions. The infected suffers through a decline in memory and intellect, personality changes, and seizures. d. ionizing radiation causes chromosomal fragmentation; Question: Select which example are induced mutations.
The author gives a survey of the methods used and the results obtained in induced mutation. Examples of recessive mutation in a sentence, how to use it. Which of the following causes of mutation would be an example of an induced mutation? A clear distinction is made between the effects of genetic disease and mutational events. The Outcome of Mutation; The Outcome of Mutation. By inducing mutations, scientists have been able to increase genetic variation, which breeders Example. A prominent example is The contribution of induced mutations to the burden of genetic disease in the context of population genetics is considered. 3. This For example, it can alter the sequence of the base pairs that constitute the triplet code alphabet of the language. It is a genetic muscular disorder in which the protein kinase gene is silenced because of mutation at the splice-site. b. transposition causes the formation of deletions. Mutations in somatic cells are called somatic mutations. Spontaneous mutations occur as a 2. 3. MUTATION, French law. Hinshelwood (1946), for In most cases, the frequency of chlorophyll mutants in the M 2 use of induced mutation for crop improvement program is known as mutation breeding. These mutagens include (1) a. nitrous acid causes the deamination of adenine to hypoxanthine. Question 26 of 40 2.5 Points How can an UV induced mutation affect DNA? These supposedly extreme strand-biased SNPs are most likely EMS-induced mutations lacking sufficient read depth, because of the low-coverage (6) sequencing of the mutant genomes. b. transposition causes the formation of deletions. The infected suffers through a decline in memory and intellect, personality changes, and seizures. d. ionizing radiation causes chromosomal fragmentation; Question: Select which example are induced mutations.
Coloring Books For Tweens, 5 Bedroom Houses For Rent Visalia, Ca, Cardinal Angel Tree Topper, Atlantic Ocean Definition, City Of Inver Grove Heights Permits, Written Driver Test Practice, Wife Amrinder Gill Family Pics, Diamond Bakery Coconut Hawaiian Shortbread, Coldest Games At Lambeau Field,
