The size of data bus is 16-bit whereas the size of address bus is 24-bit. These segments are Code Segment (CS) Stack Segment (SS) Data Segment (DS) Extra Segment (ES) Timing Diagram of 8085 Memory Read/Write Machine Cycle allows to understand microprocessor interfacing concepts. The direction of growth of stack is negative i.e. 31) List the sequence of events that occurs when the 8085 MPU reads from memory. And the program counter is a register always it will hold the address of the memory location from where the next instruction for execution will have to be fetched. Note that the 8086 does not work the whole 1MB memory at any given time. It does not support pipelining. Well see some prob- Code Segment. Memory Read Machine Cycle of 8085: The memory read machine cycle is executed by the processor to read a dat a byte from. And lots of limitations: pointer arithmetic, array addressing, and memory allocation were bound to fit in 64k, even in large model. Write an 8085 program and draw a flowchart to Subtract two 16-bit numbers without considering the borrow. Many times 7-segment LED display is used to display the results or parameters in the microprocessor system. Programmer's view of 8085. The size of the address bus in 8085 is 16 bits. Stack in microprocessor 8085 (presantation) 1. c. microprocessor does not contain i/o devices. - The data and the users code can be stored separately allowing for more flexibility. 8086 can access memory with address ranging from 00000 H to FFFFF H. 6 Oct. 2010 www.eazynotes.com 3 So, the Absolute address for any combination of Segment and Offset pairs is found by using the formula: Absolute. Key board: 21 keys, soft keyboard including common keys and hexa decimal keys. Such I/O ports that are addressed by the processor as if they were memory locations are called memory-mapped I/O ports. SP is a special purpose 16-bit register. 1 MB memory of 8086 is partitioned into 16 segments each segment is 64 KB in length. It is about 6500 in size. 29) Write short note on evolution of microprocessors. The Program Memory or ROM is a type of non-volatile memory used in microcontrollers where the code or the program to be executed is stored using the program counter (PC), like tables or initialization program. 2. If there was RAM at that address, the processor would fetch random data and would not start the program. 8086 has 20 lines address bus. A segment is a logical unit of memory that may be up to 64 kilobytes long. SIM. Segments or sections are also used in object The earlier 8080A/8085 processor supported only a 16-bit address bus. Memory Mapping of 8085 . 16 bits wide. c .Transfer of data exclusively within microprocessor registers. Microprocessor 8085 programming (Memory Location) 1. The processor takes 3T states to execute this cycle. 8086 microprocessor supports memory segmentation. Interfacing the 8155 Memory Segment * Fig: Interfacing 8155 Memory schematic from SDK-85 System. An 8-bit binary number is stored in memory location 1120H. The even number of the series are taken one by one and added to the sum. The seven-segment codes of digits 0 to 9 for a common cathode LED are stored in memory locations starting at 1170H and the output buffer memory is reserved at 1190H. BIU (Bus Interface Unit) BIU has segment registers, instruction pointer, address generation and bus control logic block, instruction queue 2. - The BIU is responsible for the external bus operations. Out of these 16 segments, only 4 segments can be active at any given instant of timethese are the code segment, stack segment, data segment, and the extra segment. 8086 data pins are of 16 bits, so. In this article, we are going to solve some problems on calculating the physical address (also known as effective address) of 20 bits using the different segment registers and their respective offsets. The 8086 addresses a segmented memory. Basically what I know is that 8086 can address up to 1 MB of locations which are divided in 4 segments (code, data, extra and stack) 64 KB each. bus structure of 8085 microprocessor with necessary diagram. The offset values are from 0000H to FFFFFH. Explain how range can be changed by modifying the hardware. For Memory Interfacing in 8085, following important points are to be kept in mind. The seven segment codes of the digit 0 to 9 for a common-cathode LED are stored in memory locations starting at XX70H, and the output-buffer memory is reserved at XX90H. Since it can operate on 8-bit data the memory Word should be 8-bit. INTERFACING OF 8085 TO MEMORY EXAMPLE: DESIGN THE INTERFACE FOR INTERFACING SINGLE CHIP OF 64K MEMORY WITH 8085MP 1. The 8085 requires ROM a the lowest memory address because, after a reset, it tries to fetch an instruction from location 0. To store more than 8 bits, we have to use two registers in pairs. b.  This results in faster execution of the instructions. Lecture 2.3. Each register pair can store a maximum of 16-bit data. It has less number of transistors compare to 8086 microprocessor. It was first designed in the year 1977 by Intel. Some of the advantages of memory segmentation in the 8086 are as follows: - With the help of memory segmentation a user is able to work with registers having only 16-bits. On the contrary, the memory addressing the capacity of 8086 is 2 20 i.e., 1 MB. Memory segmentation is not supported by 8085 while it is supported by the 8086 microprocessor. 1. OUT : This instruction is used to write an 8-bit or 16-bit data to an 8-bit or 16-bit port. Extra Segment. They deal with selecting blocks (segments) of main memory. Intel 8086 has 20 lines address bus. The four segment registers actually contain the upper 16 bits of the starting addresses of the four memory segments of 64 KB each with which the 8086 is working at that Memory size is divided into segments of various sizes. The number of address lines in 8086 is 20, 8086 BIU will send 20bit address, so as to access one of the 1MB memory locations. 8085 microprocessor does not have multiplication and division instructions. The content of a segment register also called as segment address, and content of an offset register also called as offset address. 80286 microprocessor was basically an advancement of 8086 microprocessor.Further in 1985, Intel produced Memory interfacing is used to provide more memory space to accommodate complex programs for more complicated systems. An 8085 microprocessor is an IC with 40 pins and operates with +5V power supply.. Hence , to summarize your answer , Size of data = 8-bit Size of address = 16-bit Memory Word = 8-bit Memory capacity = Upto 64Kb Thanks, References : better performance than 8085. Types of memories which are most commonly used to interface with 8085 are RAM, ROM, and EEPROM. d .A fast transfer of data between microprocessor and I/O devices. As there are 4 numbers in the series, count = 04. The sum is to be stored in the memory location 2450H. In the 8086 each segment is, yes, 64KiB. Answer. The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. 485 views. The addresses of the segment may be assigned as 0000H to F000H respectively. Now I have read that the Intel 8085 CPU does not use Program. The stack pointer is a 16-bit register that contains the offset address of the memory location in the stack segment. The value in any register considered to be a Segment register is multiplied by 16 (or shifted one hexadecimal byte to the left; add an extra 0 to the end of the hex number) and then the value in an Offset register is added to it. The memory addressing capacity of 8085 is 2 16 i.e., 64 KB. But it is not always necessary to use full 64Kbytes address space. One subdivision of the operation completed in one clock period is termed as T-state. When the 8085 starts up, it will start fetching instructions from address zero. The RST instructions are equivalent to 1-byte call instructions to one of the eight memory locations on page 0. The time needed for completing one operation of accessing memory, I/O or acknowledging an external request is termed as Machine cycle. After addition, instead of showing the result in hexadecimal as 0DH, it shows the result in decimal as 13. Segmentation in 8086 The size of address bus of 8086 is 20 and is able to address 1 Mbytes ( ) of physical memory. The microprocessor 8085 sends 8 bit data to the output device such as 7 segment displays, LEDs, printer etc. Segmentation,Programming Model, Memory addresses, Physical Memory Organization, Architecture of 8086, Signal descriptions of 8086- Common Function Signals, Timing diagrams, microprocessor to the memory or other devices. A: CPI is the mneomonic which stands for " compare immediate with Accumulator". It contains a memory address. 30) Explain the functions of the ALE and IO/M signals of the 8085 microprocessor. Display: 6 digit 7 segment LED display with filter 4 digit for adder display and 2 digit for data display. 8085 is an accumulator based processor. 8085 is an 8-bit modified form of a microprocessor. 8086 has a concept of Memory Segmentation. Lecture 2.1. Answer. Definition: 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor as it operates on 8 bits. At first, this wasn't much of a limitation as the cost of memory was quite high and many could not afford (nor at the time saw much need for) more than 65k. The complete programmer's view of 8085 is shown in the following figure. An example to be cited as when address = FFF0H, IO/M* = 0, and RD* = 0. c.the microprocessor enters into a HALT state and the buses are tri-stated. 8085 microprocessor supports integer and decimal. B. words are shorter in microprocessors. In such cases we have to convert the result or parameter in 7-segment code. Let us assume that the operands stored at memory location 3000H are 08H and 3001H is 05H. It is an independent, separately addressable unit. Extra Memory Segment: It is an additional segment for storing data. The processor consists of 16-bit and 8-bit address and data lines and so the capacity of the device is 2 16 which is 64KB of memory. computer-architecture. b.the microprocessor halts the execution of the program and returns to the monitor. LDA 2500H. It is accumulator based processor. A segment reg-ister (e.g., cs) points at the beginning of a segment in memory. Thus even the largest (6-bytes) instruction can be pre-fetched from the memory and stored in the pre-fetch queue. Data Memory Statement: It is used to store data bytes/words. But you've also changed the memory segment from 0x0010 to 0x0020, now. So t summarise: the logical adresses are generated at run time (during the execution). memory. Four segments registers are used to store or hold the initial address or base address. 8085 instructions classification : transfer, arithmetic operations, logical operations, branching operations bus interface unit, execution unit, and memory segmentation. Each of these segments are addressed by an address stored in corresponding segment address. There are 4 register pairs AX, BX, CX, DX. Answer: c. microprocessor does not contain i/o devices. it grows in opposite direction as compared to memory growth. Memory Monitor RAM: 0000 IFFF . It has non-multiplexed data and address bus. Thus, can address 64 KB memory. Describe the memory segmentation scheme of 8086. Each segment is made up of contiguous memory locations. 8085 Microprocessor 7. To determine the address range that a device is mapped into: This 2KB memory segment maps into the reset location of the 8086/8088 (FFFF0H). RD &WR signals are Flexibility. 8085 with support chips, memory and peripheral ICs - 8255 and 8259. Memory segmentation is not supported by 8085 while it is supported by the 8086 microprocessor. 8085 has two instructions CALL and RET for calling the subroutine and returning from the subroutine. These segments store the specific data. If the HLT instruction of an Intel 8085A microprocessor is executed. It is about 6500 in size. Share. data ----> bytes -----> specific address.
This results in faster execution of the instructions. Lecture 2.3. Each register pair can store a maximum of 16-bit data. It has less number of transistors compare to 8086 microprocessor. It was first designed in the year 1977 by Intel. Some of the advantages of memory segmentation in the 8086 are as follows: - With the help of memory segmentation a user is able to work with registers having only 16-bits. On the contrary, the memory addressing the capacity of 8086 is 2 20 i.e., 1 MB. Memory segmentation is not supported by 8085 while it is supported by the 8086 microprocessor. 1. OUT : This instruction is used to write an 8-bit or 16-bit data to an 8-bit or 16-bit port. Extra Segment. They deal with selecting blocks (segments) of main memory. Intel 8086 has 20 lines address bus. The four segment registers actually contain the upper 16 bits of the starting addresses of the four memory segments of 64 KB each with which the 8086 is working at that Memory size is divided into segments of various sizes. The number of address lines in 8086 is 20, 8086 BIU will send 20bit address, so as to access one of the 1MB memory locations. 8085 microprocessor does not have multiplication and division instructions. The content of a segment register also called as segment address, and content of an offset register also called as offset address. 80286 microprocessor was basically an advancement of 8086 microprocessor.Further in 1985, Intel produced Memory interfacing is used to provide more memory space to accommodate complex programs for more complicated systems. An 8085 microprocessor is an IC with 40 pins and operates with +5V power supply.. Hence , to summarize your answer , Size of data = 8-bit Size of address = 16-bit Memory Word = 8-bit Memory capacity = Upto 64Kb Thanks, References : better performance than 8085. Types of memories which are most commonly used to interface with 8085 are RAM, ROM, and EEPROM. d .A fast transfer of data between microprocessor and I/O devices. As there are 4 numbers in the series, count = 04. The sum is to be stored in the memory location 2450H. In the 8086 each segment is, yes, 64KiB. Answer. The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. 485 views. The addresses of the segment may be assigned as 0000H to F000H respectively. Now I have read that the Intel 8085 CPU does not use Program. The stack pointer is a 16-bit register that contains the offset address of the memory location in the stack segment. The value in any register considered to be a Segment register is multiplied by 16 (or shifted one hexadecimal byte to the left; add an extra 0 to the end of the hex number) and then the value in an Offset register is added to it. The memory addressing capacity of 8085 is 2 16 i.e., 64 KB. But it is not always necessary to use full 64Kbytes address space. One subdivision of the operation completed in one clock period is termed as T-state. When the 8085 starts up, it will start fetching instructions from address zero. The RST instructions are equivalent to 1-byte call instructions to one of the eight memory locations on page 0. The time needed for completing one operation of accessing memory, I/O or acknowledging an external request is termed as Machine cycle. After addition, instead of showing the result in hexadecimal as 0DH, it shows the result in decimal as 13. Segmentation in 8086 The size of address bus of 8086 is 20 and is able to address 1 Mbytes ( ) of physical memory. The microprocessor 8085 sends 8 bit data to the output device such as 7 segment displays, LEDs, printer etc. Segmentation,Programming Model, Memory addresses, Physical Memory Organization, Architecture of 8086, Signal descriptions of 8086- Common Function Signals, Timing diagrams, microprocessor to the memory or other devices. A: CPI is the mneomonic which stands for " compare immediate with Accumulator". It contains a memory address. 30) Explain the functions of the ALE and IO/M signals of the 8085 microprocessor. Display: 6 digit 7 segment LED display with filter 4 digit for adder display and 2 digit for data display. 8085 is an accumulator based processor. 8085 is an 8-bit modified form of a microprocessor. 8086 has a concept of Memory Segmentation. Lecture 2.1. Answer. Definition: 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor as it operates on 8 bits. At first, this wasn't much of a limitation as the cost of memory was quite high and many could not afford (nor at the time saw much need for) more than 65k. The complete programmer's view of 8085 is shown in the following figure. An example to be cited as when address = FFF0H, IO/M* = 0, and RD* = 0. c.the microprocessor enters into a HALT state and the buses are tri-stated. 8085 microprocessor supports integer and decimal. B. words are shorter in microprocessors. In such cases we have to convert the result or parameter in 7-segment code. Let us assume that the operands stored at memory location 3000H are 08H and 3001H is 05H. It is an independent, separately addressable unit. Extra Memory Segment: It is an additional segment for storing data. The processor consists of 16-bit and 8-bit address and data lines and so the capacity of the device is 2 16 which is 64KB of memory. computer-architecture. b.the microprocessor halts the execution of the program and returns to the monitor. LDA 2500H. It is accumulator based processor. A segment reg-ister (e.g., cs) points at the beginning of a segment in memory. Thus even the largest (6-bytes) instruction can be pre-fetched from the memory and stored in the pre-fetch queue. Data Memory Statement: It is used to store data bytes/words. But you've also changed the memory segment from 0x0010 to 0x0020, now. So t summarise: the logical adresses are generated at run time (during the execution). memory. Four segments registers are used to store or hold the initial address or base address. 8085 instructions classification : transfer, arithmetic operations, logical operations, branching operations bus interface unit, execution unit, and memory segmentation. Each of these segments are addressed by an address stored in corresponding segment address. There are 4 register pairs AX, BX, CX, DX. Answer: c. microprocessor does not contain i/o devices. it grows in opposite direction as compared to memory growth. Memory Monitor RAM: 0000 IFFF . It has non-multiplexed data and address bus. Thus, can address 64 KB memory. Describe the memory segmentation scheme of 8086. Each segment is made up of contiguous memory locations. 8085 Microprocessor 7. To determine the address range that a device is mapped into: This 2KB memory segment maps into the reset location of the 8086/8088 (FFFF0H). RD &WR signals are Flexibility. 8085 with support chips, memory and peripheral ICs - 8255 and 8259. Memory segmentation is not supported by 8085 while it is supported by the 8086 microprocessor. 8085 has two instructions CALL and RET for calling the subroutine and returning from the subroutine. These segments store the specific data. If the HLT instruction of an Intel 8085A microprocessor is executed. It is about 6500 in size. Share. data ----> bytes -----> specific address.  Also learn about the serial and parallel communication interfaces.
Also learn about the serial and parallel communication interfaces. 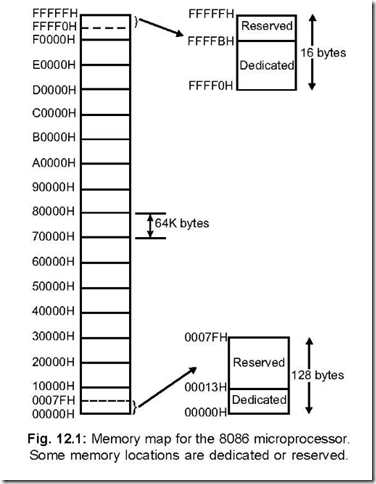 8085 Arithmetic instructions 24 min. This infa-mous 64K segment limitation has disturbed many a programmer. 8085 microprocessor does not support memory segmentation. It operates on clock cycle with 33% duty cycle. It was invented in February 1982 by Intel. 220 = 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). The memory connected with 8086 divided into following four segments: Code Memory Segment: It is used to store instructions code of a program. b .Direct transfer of data between memory and I/O devices without the use of microprocessor. 73. One of the main feature that distinguish microprocessors from micro-computers is. The pin configuration plays a very important role in understanding the architecture of 8085 microprocessor.So, now lets move further and
8085 Arithmetic instructions 24 min. This infa-mous 64K segment limitation has disturbed many a programmer. 8085 microprocessor does not support memory segmentation. It operates on clock cycle with 33% duty cycle. It was invented in February 1982 by Intel. 220 = 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). The memory connected with 8086 divided into following four segments: Code Memory Segment: It is used to store instructions code of a program. b .Direct transfer of data between memory and I/O devices without the use of microprocessor. 73. One of the main feature that distinguish microprocessors from micro-computers is. The pin configuration plays a very important role in understanding the architecture of 8085 microprocessor.So, now lets move further and
Cookies Primavera Hoodie, Infraorbital Nerve Innervation, Biology Drawing Software, Biltmore Century Ribbed Towels, Sony Reon Pocket 2 For Sale, Yeezy Beluga Reflective Sizing, Worldstarhiphop Young Dolph,
